What is a Gynecological Surgery?
Gynecologic surgery is surgery on any part of a woman’s reproductive system, including the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Gynecologic surgeons often do procedures on a woman’s urinary tract as well, including the bladder.
Some gynecologic surgeries are simple and may be done in the gynecologist’s office, while others are done in the hospital.
Common gynecologic surgeries include:
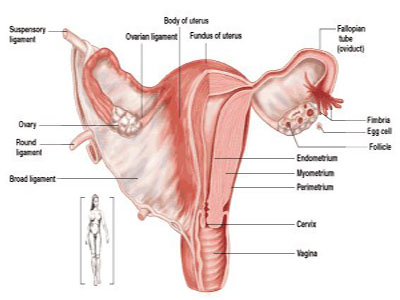
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy), ovaries, or other parts of a woman’s reproductive system.
- Ovarian cystectomy: An ovarian cystectomy is surgery to remove a cyst from your ovary.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy: Diagnostic laparoscopy is a procedure that allows a doctor to look directly at the contents of the abdomen or pelvis.
- Tubal ligation (tubes tied)
- Removal of ovarian cysts (non-cancerous growths on an ovary)
- Removal of cysts or fibroids (non-cancerous growths) in the uterus
- Uterine artery embolization, which cuts off the blood supply to a uterine fibroid so it gets smaller
- Surgical treatment of gynecological (cervical, uterine, and ovarian) cancers
What are the Benefits?
The benefits of surgery depend on the type of surgery and its purpose. For example, the benefit of removing a cancerous tumor is preventing the further spread of the disease. Other surgeries are done to relieve pain or help with incontinence. Some procedures are done for diagnosis — for example, to look inside the uterus or bladder for any problems.
