What is an Endoscopy Procedure?
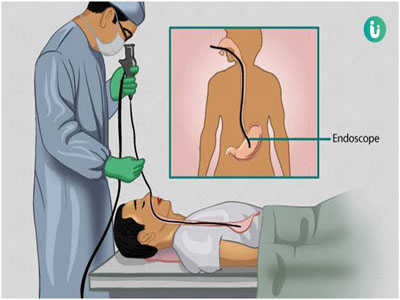
An endoscopy is a procedure in which your doctor uses specialized instruments to view and operate on the internal organs and vessels of your body. It allows surgeons to see problems within your body without making large incisions.
A surgeon inserts an endoscope through a small cut or an opening in the body such as the mouth. An endoscope is a flexible tube with an attached camera that allows your doctor to see. Your doctor can use forceps and scissors on the endoscope to operate or remove tissue for biopsy
Types Of Endoscopy
- Upper G.I. Scopy
- Colono-Scopy
- E.R.C.P
- Capsule Endoscopy
When to use Endoscopy
- Upper G.I. Scopy
- Hematemesis
- Malena
- Obseure G.I. Bleed
- To evaluate anemia
When to Use Colonoscopy
- P.R Bleed
- Stool occult blood positive
- Chronic Diarrhoea
- Chronic Constipation
When to do E.R.C.P : (Used to see abnormalities of the small intestine)
- Obstructive Jaundice
- Periampullary Carcinoma
- C.B.D Stones
Symptoms of Endoscopy
- inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease
- stomach ulcer
- chronic constipation
- pancreatitis
- gallstones
- unexplained bleeding in the digestive tract
- tumors
- infections
- blockage of the esophagus
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- hiatal hernia
- unusual vaginal bleeding
- blood in your urine
- other digestive tract issues
Esophageal Biopsy
Usually, if a suspected esophageal cancer is found on endoscopy or an imaging test, it is biopsied. In a biopsy, the doctor removes a small piece of tissue with a cutting instrument passed through the scope.
Stomach Biopsy for Cancer & H. Pylori Infection
A gastric tissue biopsy and culture are laboratory tests that examine stomach tissue. These tests are typically carried out to determine the cause of a stomach ulcer or other troublesome stomach symptoms. “Gastric tissue biopsy” is the term used for the examination of tissue removed from your stomach.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a bacterial infection that causes stomach inflammation (gastritis), peptic ulcer disease, and certain types of stomach cancer. The infection is caused by a type of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
Duodenal Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a piece of body tissue so that the cells within the tissue can be viewed under a microscope. A duodenal biopsy is the removal of tissue from the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine/bowel).
Endoscopic Variceal Band Ligation(EVLT)
EVL is performed using a banding device attached to the tip of the endoscope. The varix is aspirated into the banding chamber, and a tripwire dislodges a rubber band carried on the banding chamber, ligating the entrapped varix. One to 3 bands are applied to each varix, resulting in thrombosis.
Foreign Body Removal From Esophagus & Stomach
Endoscopic foreign body removal is a minimally invasive procedure to remove items that have been swallowed and become stuck in the digestive tract. (If an object becomes lodged in the airway and obstructs breathing, emergency medical attention is required.)
Colonoscopic Biopsy
If your doctor thinks an area needs further evaluation, he or she might pass an instrument through the colonoscope to obtain a biopsy (a small sample of the colon lining) to be analyzed. Biopsies are used to identify many conditions, and your doctor will often take a biopsy even if he or she doesn’t suspect cancer.
Colonoscopic Snare Polypectomy
The polyp is pulled away from its base into the lumen tenting the colon wall to avoid burning the adjacent deep colon layers[11]. A snare can be either hot or cold in that it can be supplemented with electrocautery or not. During hot snaring, the endoscopist’s assistant should close the snare slowly and gently.
